Waste water treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and converting it into an effluent that can be returned to the environment or reused for various purposes. This involves several stages including pre-treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, and sometimes advanced treatment, which may include physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove pollutants such as organic matter, nutrients, heavy metals, and pathogens. The ultimate goal of waste water treatment is to produce safe and clean water that meets discharge standards and protects the environment and public health.
1. What is waste water treatment ?
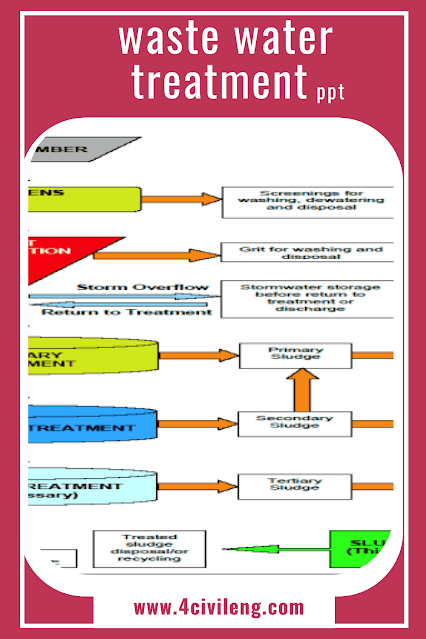
Waste water treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater to make it safe for release into the environment or for reuse. The process typically involves several stages including:
Pre-treatment: removal of large objects such as rags, sticks, and debris from the wastewater.
Primary treatment: settling of solids and removal of floating matter by gravity.
Secondary treatment: biological treatment using microorganisms to break down organic matter and remove pollutants.
Tertiary treatment: additional physical, chemical or biological processes to remove specific pollutants and improve the quality of the treated wastewater.
The goal of waste water treatment is to produce effluent that meets discharge standards and protects the environment and public health.
2. What are the main types of waste water treatment ?
The main types of wastewater treatment are:
- Physical treatment Chemical treatment Biological treatment Sludge treatment
- Physical treatment involves physical processes such as screening, sedimentation, and flotation to remove solid waste.
- Chemical treatment uses chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and disinfectants to remove pollutants.
- Biological treatment employs microorganisms to break down organic matter and remove pollutants.
- Sludge treatment involves the processing of residual solids generated from physical, chemical, and biological treatments.
3. What is the significance of waste water treatment ?
Waste water treatment is important because it helps to protect public health and the environment by removing harmful pollutants and pathogens from wastewater before it is released into the environment. Treated wastewater can also be reused for agricultural or industrial purposes, conserving water resources. By treating waste water, we can also reduce the risk of contamination of drinking water supplies and prevent the spread of diseases. Additionally, proper waste water treatment can reduce the negative impacts on aquatic life and ecosystems, preserving the balance of the environment.
4. What are the environmental benefits of waste water treatment ?
Waste water treatment provides several environmental benefits, including:
- Reduction of water pollution: Treated waste water helps to reduce the amount of pollutants, such as chemicals and pathogens, that are released into the environment.
- Protection of aquatic life: By removing harmful pollutants, waste water treatment helps to preserve the health of aquatic ecosystems and the species that rely on them.
- Preservation of drinking water sources: Treating waste water helps to prevent contamination of drinking water sources, ensuring that they remain safe and clean for human consumption.
- Conservation of water resources: Treated waste water can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and other purposes, conserving fresh water resources.
- Climate change mitigation: Waste water treatment can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using biogas generated during the treatment process as an energy source.
In summary, waste water treatment is crucial for maintaining the health of our environment, preserving natural resources, and promoting sustainable development.
5. What are the economic benefits of waste water treatment? 6. What are the social benefits of waste water treatment ?
Economic benefits of waste water treatment:
- Job creation: The waste water treatment industry can create job opportunities in fields such as engineering, construction, and operations.
- Increased property values: Proper waste water treatment can lead to increased property values in nearby areas, as it helps to maintain a clean and safe environment.
- Cost savings: Treating waste water can be less expensive than the cost of cleaning up after water pollution has occurred.
- Revenue generation: Treated waste water can be sold or reused for agricultural or industrial purposes, generating revenue for communities.
- Energy production: Waste water treatment facilities can use biogas produced during the treatment process as a source of renewable energy, reducing the need for non-renewable energy sources.
Social benefits of waste water treatment:
- Improved public health: Treating waste water helps to remove pathogens and pollutants, reducing the risk of water-borne diseases and improving public health.
- Enhanced quality of life: Proper waste water treatment can improve the overall quality of life by reducing unpleasant odors, preserving natural resources, and promoting clean and safe environments.
- Increased community pride: Waste water treatment facilities can provide a sense of pride for communities, as they demonstrate a commitment to environmental sustainability and public health.
- Better environmental stewardship: By treating waste water, communities can show their commitment to environmental stewardship and their responsibility for the health of the planet.
Overall, waste water treatment has a positive impact on both the economy and society, providing benefits in terms of job creation, cost savings, improved public health, and enhanced quality of life.
find here waste water treatment ppt free download











.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.webp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)